CAVITATION AND BUBBLE DYNAMICS
by Christopher Earls Brennen © Oxford University Press 1995
Nomenclature
ROMAN LETTERS
| a | Amplitude of wave-like disturbance |
| A | Cross-sectional area or cloud radius |
| b | Body half-width |
| B | Tunnel half-width |
| c | Concentration of dissolved gas in liquid, speed of sound, chord |
| ck | Phase velocity for wavenumber k |
| cP | Specific heat at constant pressure |
| CD | Drag coefficient |
| CL | Lift coefficient |
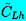 , , 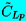 | Unsteady lift coefficients |
| CM | Moment coefficient |
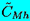 , , 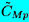 | Unsteady moment coefficients |
| Cij | Lift/drag coefficient matrix |
| Cp | Coefficient of pressure |
| Cpmin | Minimum coefficient of pressure |
| d | Cavity half-width, blade thickness to spacing ratio |
| D | Mass diffusivity |
| f | Frequency in Hz. |
| f | Complex velocity potential, φ+iψ |
| fN | A thermodynamic property of the phase or component, N |
| Fr | Froude number |
| g | Acceleration due to gravity |
| gx | Component of the gravitational acceleration in direction, x |
| gN | A thermodynamic property of the phase or component, N |
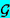 (f) (f) | Spectral density function of sound |
| h | Specific enthalpy, wetted surface elevation, blade tip spacing |
| H | Henry's law constant |
| Hm | Haberman-Morton number, normally gμ4/ρS3 |
| i,j,k | Indices |
| i | Square root of -1 in free streamline analysis |
| I | Acoustic impulse |
| I* | Dimensionless acoustic impulse, 4πI {\cal R} / ρL U∞ RH2 |
| IKi | Kelvin impulse vector |
| j | Square root of -1 |
| k | Boltzmann's constant, polytropic constant or wavenumber |
| kN | Thermal conductivity or thermodynamic property of N |
| KG | Gas constant |
| Kij | Added mass coefficient matrix, 3Mij/4ρπR3 |
| Kc | Keulegan-Carpenter number |
| Kn | Knudsen number, λ/2R |
| ℓ | Typical dimension in the flow, cavity half-length |
| L | Latent heat of vaporization |
| m | Mass |
| mG | Mass of gas in bubble |
| mp | Mass of particle |
| Mij | Added mass matrix |
| n | Index used for harmonics or number of sites per unit area |
| N(R) | Number density distribution function of R |
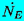 | Cavitation event rate |
| Nu | Nusselt number |
| p | Pressure |
| pa | Radiated acoustic pressure |
| ps | Root mean square sound pressure |
| pS | A sound pressure level |
| pG | Partial pressure of gas |
| P | Pseudo-pressure |
| Pe | Peclet number, usually WR/αL |
| q | Magnitude of velocity vector |
| qc | Free surface velocity |
| Q | Source strength |
| r | Radial coordinate |
| R | Bubble radius |
| RB | Equivalent volumetric radius, [3τ/4π]1/3 |
| RH | Headform radius |
| RM | Maximum bubble radius |
| RN | Cavitation nucleus radius |
| RP | Nucleation site radius |
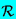 | Distance to measurement point |
| Re | Reynolds number, usually 2WR/νL |
| s | Coordinate measured along a streamline or surface |
| s | Specific entropy |
| S | Surface tension |
| St | Strouhal number, 2fR/W |
| t | Time |
| tR | Relaxation time for relative motion |
| t* | Dimensionless time, t/tR |
| T | Temperature |
| u,v,w | Velocity components in cartesian coordinates |
| ui | Velocity vector |
| ur,uθ | Velocity components in polar coordinates |
| u′ | Perturbation velocity in x direction, u-U∞ |
| U, Ui | Fluid velocity and velocity vector in absence of particle |
| V, Vi | Absolute velocity and velocity vector of particle |
| U∞ | Velocity of upstream uniform flow |
| w | Complex conjugate velocity, u-iv |
| w | Dimensionless relative velocity, W/W∞ |
| W | Relative velocity of particle |
| W∞ | Terminal velocity of particle |
| We | Weber number, 2ρW2R/S |
| z | Complex position vector, x+iy |
GREEK LETTERS
| α | Thermal diffusivity, volume fraction, angle of incidence |
| β | Cascade stagger angle, other local variables |
| γ | Ratio of specific heats of gas |
| Γ | Circulation, other local parameters |
| δ | Boundary layer thickness or increment of frequency |
| δD | Dissipation coefficient |
| δT | Thermal boundary layer thickness |
| ε | Fractional volume |
| ζ | Complex variable, ξ+iη |
| η | Bubble population per unit liquid volume |
| η | Coordinate in ζ-plane |
| θ | Angular coordinate or direction of velocity vector |
| κ | Bulk modulus of compressibility |
| λ | Mean free path of molecules or particles |
| Λ | Accommodation coefficient |
| μ | Dynamic viscosity |
| ν | Kinematic viscosity |
| ξ | Coordinate in ζ-plane |
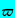 | Logarithmic hodograph variable, χ+iθ |
| ρ | Density |
| σ | Cavitation number |
| σc | Choked cavitation number |
| σij | Stress tensor |
| Σ | Thermal parameter in bubble growth |
| τ | Volume of particle or bubble |
| ø | Velocity potential |
| ø′ | Acceleration potential |
| φ | Fractional perturbation in bubble radius |
| Φ | Potential energy |
| χ | log(qc/|w|) |
| ψ | Stream function |
| ω | Radian frequency |
| ω* | Reduced frequency, ωc/U∞ |
SUBSCRIPTS
On any variable, Q:
| Qo | Initial value, upstream value or reservoir value |
| Q1,Q2,Q3 | Components of Q in three Cartesian directions |
| Q1,Q2 | Values upstream and downstream of a shock |
| Q∞ | Value far from the bubble or in the upstream flow |
| QB | Value in the bubble |
| QC | Critical values and values at the critical point |
| QE | Equilibrium value or value on the saturated liquid/vapor line |
| QG | Value for the gas |
| Qi | Components of vector Q |
| Qij | Components of tensor Q |
| QL | Saturated liquid value |
| Qn | Harmonic of order n |
| QP | Peak value |
| QS | Value on the interface or at constant entropy |
| QV | Saturated vapor value |
| Q* | Value at the throat |
SUPERSCRIPTS AND OTHER QUALIFIERS
On any variable, Q:
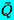 | Mean value of Q or complex conjugate of Q |
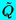 | Complex amplitude of oscillating Q |
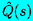 | Laplace transform of Q(t) |
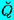 | Coordinate with origin at image point |
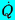 | Rate of change of Q with time |
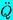 | Second derivative of Q with time |
| Q+,Q- | Values of Q on either side of a cut in a complex plane |
| δQ | Small change in Q |
| Re{Q} | Real part of Q |
| Im{Q} | Imaginary part of Q |
UNITS
In most of this book, the emphasis is placed on the nondimensional parameters that govern the phenomenon being discussed. However, there are also circumstances in which we shall utilize dimensional thermodynamic and transport properties. In such cases the International System of Units will be employed using the basic units of mass (kg), length (m), time (s), and absolute temperature (K); where it is particularly convenient units such as a joule (kg m2/s2) will occasionally be used.
Last updated 12/1/00.
Christopher E. Brennen